ACCEPTABLE QUALITY LEVEL (AQL)
Most of the acceptance decisions of the apparel shipments for the export market are made on the basis of AQL based sampling plans. If AQL pass that means goods are in acceptable quality level and goods get clearance to ship. The AQL level varies process to process, product to product and even buyer to buyer in garment industry. In general cases the buyer will determine which sampling plan and what AQL to follow. Usually the following five parts depends on acceptance of quality products;
- Lot Size
- Sample Size
- Acceptable Quality Level
- Accept Number
- Reject Number
There are three types of sampling plans: i.e. single, double and multiple sampling plans.
Each sampling plan can be performed at three levels, i.e. normal, tightened and reduced, depending on inspection requirements and quality of the products. The apparel industry mainly uses single sampling plans for the acceptance decisions. However, a few buyers also use double sampling procedure.
In single sample based on AQL table you randomly draw a sample consisting of specified number of garments from a lot. The sample plan also provides the number maximum allowed defective pieces. If the defective pieces are less than allowed number, the lot is accepted and if the number of defective pieces is greater than allowed the lot is rejected. However, specific buyers may accept the goods even the defectives quantity is more than AQL. QIV always appreciate in action to segregate the defective production and make correction these defective or be transparent to the ultimate consumers about the defects and let them to decide whether they will buy or not.
The most commonly used AQL is a major 2.5 Minor 4.0. The AQL random sampling inspection is derived from the mathematical theory of probability and is based on the sampling these defined in military standard 105D (MIL-STD – 105D) also known as (BS 6001, ISO 2859, DIN 40080) which provides the sampling plans; and these determine the number of samples of being inspected in lot size, in addition to indicating and the acceptable quality level (AQL) which represents the maximum number of defects per hundred units that, for the purpose of the sampling inspection can be considered satisfactory as a process average.
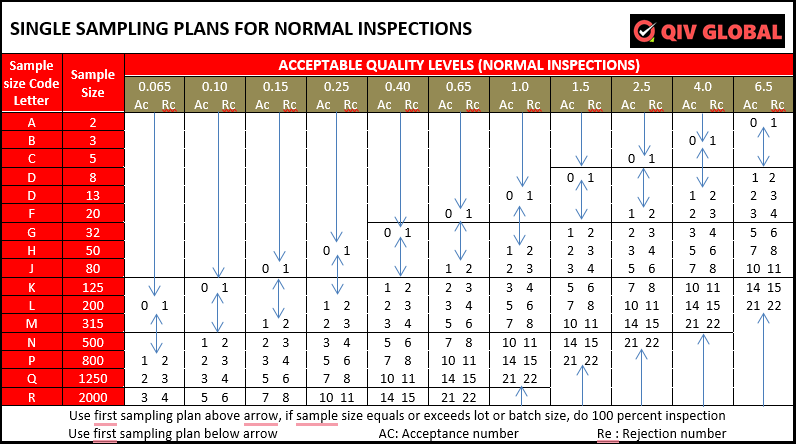
SINGLE SAMPLING PLAN – NORMAL INSPECTION
Assurance an AQL of 2.5 % and a lot size of 1200 garments and the sample size is 80 garments. If the number of defective garments found is 5 the total lot is “Acceptable” suppose if the defective garments found is 6, the total lot is “Reject/ Re-Check”.
DOUBLE SAMPLING PLAN – NORMAL INSPECTION
Assurance an AQL 4.0% and a lot size is 1200 garments and the sample size is 80 garments. If the Number of defective garments found is 7, the total lot is “Acceptable” suppose if the defective garments found is 8 the total lot is “Reject/ Re-Check”.
FOR EXAMPLE
Total garments (lot Size) 1200 garments
Sample size (selected for inspection) 80 garments
AQL 2.5 / 4.0
If the major defective found is 5 and minor defective found is 7 the total garments is “Acceptable”. If the defective exceeds (Above 5 major and 7 Minor), the total garments is Reject / Re-check.
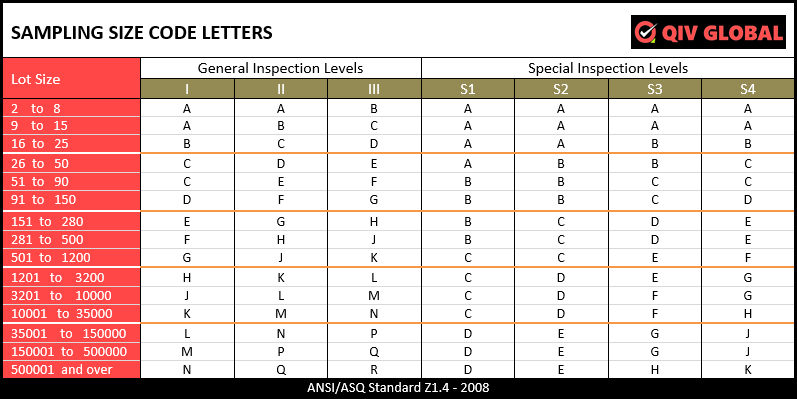
HOW TO READ AQL TABLE?
- Lot or Batch size: It indicates total how many pieces are going to be checked or inspected.
- Sample size Code letter: This code is indicative a range of batch size.
- Sample size: It means that how many pieces will be picked up for inspection from the total offered pieces (Batch).
- Ac (Accepted): The number in this column denotes that if the inspector finds up to that much defective pieces the shipment will be accepted by buyer.
- Re (Rejected): On the other hand, number in this column denotes that if the inspector finds that much defective pieces or more than the listed number, the shipment will be rejected (or asked to the manufacturer for 100% inspection and re-offer for final inspection) by buyer.
|
WHAT AQL IS NOT? |
Having known what is AQL? How does it work? How to succeed in AQL based inspections? It is equally important to now, as indicated below, what AQL is not:
- A permit to ship defective goods to the tune of agreed AQL level: AQL 4.0 does not mean that supplier has a right to send up to 4% defective merchandise to customer / buyer.
- A guarantee that all shipments passed as per AQL plan will definitely contain lower percent defective than the specified AQL. There is also no guarantee that lots with higher percentage defective will not pass on AQL inspection.
- An indicator of the quality level achieved by a manufacturer. Let us assume that the average rate of defective garments in a manufacturer’s shipment is 6%, but the AQL used by buyer for final inspection is 2.5. It is possible that the manufacturer may resort to 100% inspection of the merchandise to weed out the defective garments so that the shipment can pass the final inspection by the buyer at AQL 2.5.

